Ultra-wideband testing&certification standards of the United States/European&Canada
The characteristics of UWB technology make UWB technology occupies a great advantage in the current various indoor positioning technologies, and UWB has more and more popular prospects, countries have specific requirements for its testing and certification.
1. Detailed UWB technology and regulatory requirements of three countries
UWB technology is a wireless carrier communication technology that uses a frequency bandwidth above 1 GHz. It does not use a sinusoidal carrier, but uses nanosecond-level non-sinusoidal narrow pulses to transmit data. Therefore, it occupies a large spectrum. Although wireless communication is used, its data transmission rate can reach hundreds of megabits per second. . UWB technology can transmit signals over a very wide bandwidth. The Federal Communications Commission (FCC) of the United States stipulates that UWB technology: occupies a bandwidth of more than 500MHz in the 3.1~10.6GHz frequency band.
In February 2002, the Federal Communications Commission of the United States issued preliminary regulations on the use of spectrum and power for civilian UWB equipment. In this regulation, a communication system with a relative bandwidth greater than 0.2 or a bandwidth greater than 500 MHz at any time of transmission is called a UWB system, and UWB technology can be used for civilian commodities at the same time. Subsequently, Japan opened the ultra-wideband frequency band in August 2006.
(1) U.S. testing requirements for ultra-wideband UWB
FCC Part 15 Subpart F
(2) EU‘s test requirements for ultra-wideband UWB
ETSI EN 302 065-1
ETSI EN 302 065-2; ETSI EN 302 065-3
ETSI EN 302 065-4; ETSI EN 303 883
(3) Canada‘s test requirements for ultra-wideband UWB
RSS-220
2.the comparison of 3 kinds of indoor positioning and the positioning advantages of UWB technology.
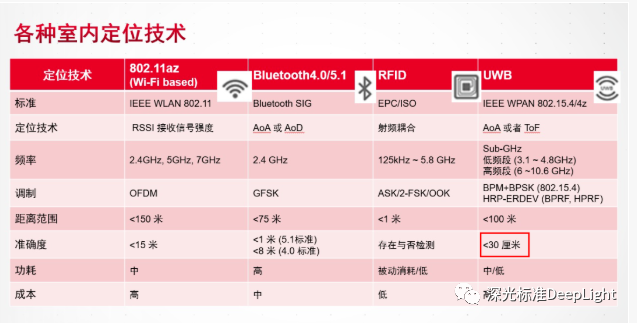
As shown in the figure above, the advantage of UWB compared with other indoor positioning is its ultra-high accuracy, accurate to the centimeter level, less than 100 meters in the range of distance accuracy error within 30 cm, the latest UWB technology can control the accuracy within 12 cm, which is simply a technical innovation for indoor positioning technology.
Another unique advantage of UWB is security. In the IEEE 802.15.4z update standard just released a few months ago, the security of UWB positioning has been improved, which can theoretically further prevent UWB-based positioning from being hacked and tampered with.
3.What is the difficulty of the ultra-wideband UWB test?
As a radio frequency technology, UWB technology should be relatively simple compared to mobile communication technologies such as 4G and 5G. So what are the test challenges?
Mainly lies in the radio frequency physical layer test; then what is the challenge of the physical layer test? Mainly in the following three aspects: high frequency, large bandwidth and different specifications.
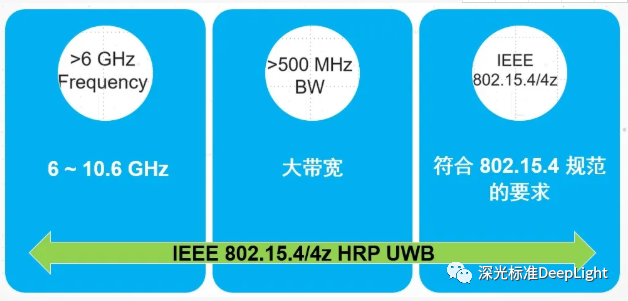
High frequency, easy to understand, the higher the frequency, the more difficult it is to make and measure the radio frequency device. The large bandwidth makes it difficult to realize the technology. Many factors need to be considered during the test, and the cost of the test equipment is relatively high;
Finally, the requirements of the test specifications, each country, each organization may have different test specifications, not only to meet the basic technical specifications, but also to meet the local test requirements, for example, European ETSI must release its own short-range equipment test specifications , The US FCC may have additional requirements; China’s National Radio Commission also has its own requirements for micro-power UWB devices. Therefore, the complexity of the test is greatly increased.
As far as the standard 802.15.4 is concerned, the RF requirements for UWB equipment are defined in Chaper 16, and various corresponding radio frequency parameters are specified, such as frequency band, channel allocation, maximum transmission power, center frequency error and maximum receiver input power. Equality, these requirements must be met, the following figure is part of the RF specification requirements.
Deeplight, with a group of strong technical experts and research teams, always keep abreast of the latest developments and technical requirements of certification, and can design the most optimized certification scheme for your products. The above is the introduction of the Deeplight standard to the UWB USEUCanada testing and certification standards. If you have any needs in this regard, please feel free to contact us for consultation!
Recommended items
-

Japan Telec certified model changes&product catalog
Japan Telec certified model changes&product catalogView more -
NRTL certification and UL standards testing
NRTL(Nationally Recognized Testing Laboratory) certification and UL standards testing is used for the safety certification of electrical and electronic products exported to the North American market.View more -

Battery IECEN 62133
The IECEN 62133 standard is mainly aimed at the safety requirements of single batteries and batteries containing alkaline or non-acid electrolytes and portable sealed single batteries and batteries (including lithium batteries, Ni-MH batteries, Ni-CD batteries, etc.). It mainly includes the testing and verification of the following items:...View more -

Google Android 12 Version GMS Certification Compatibility Document Some Basic Requirements for Handheld Device Testing
An Android handheld device is an Android device that is usually implemented by holding it in your hand, such as an mp3 player, mobile phone, or tablet. If Android device implementations meet all of the following conditions, they are classified as handheld devices, and the application of GMS certification for handheld devices requires the MADA agreement. ...View more




